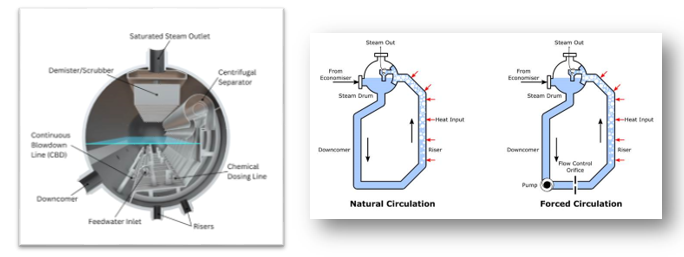
Direct fuel fired furnaces supplied by Chaman have been used in refinery operations, providing the thermal energy required to drive high temperature processes such as distillation, cracking and reforming. The evolution of petrochemical and gas production applications means that heaters are being installed in a wide variety of production units and as low carbon fuel production grows, furnaces will remain an essential part of the energy transition.
There are 3 main design types for direct flame furnaces: Cylindrical, box and cabinet. The most common type of heater is the cylindrical one with vertical coils. Cylindrical furnaces with spiral coils are also offered for smaller heater duties.
Chaman Company offers a dynamic approach by considering the design aspect for cost control and construction feasibility during assembly and installation.
Also, using our experience to provide modular furnaces for the construction of a project, from engineering to delivery and commissioning operations, it is available to all our customers.
Direct flame heaters are designed in accordance with customer and international standards such as API 560. For example:Distillation Processes - Titanium Dioxide Producer - Solvent Deasphalting - Steam Methane Reforming - Gas to Liquids (GTL) Naphtha Reforming - Waxing Units - Alkane Dehydrogenation - Styrene Monomer Production - Hydrosulfurization - Hydrocracking Isomerization - LNG - Laboratory - Thermal Cracking - Hydrotherapy